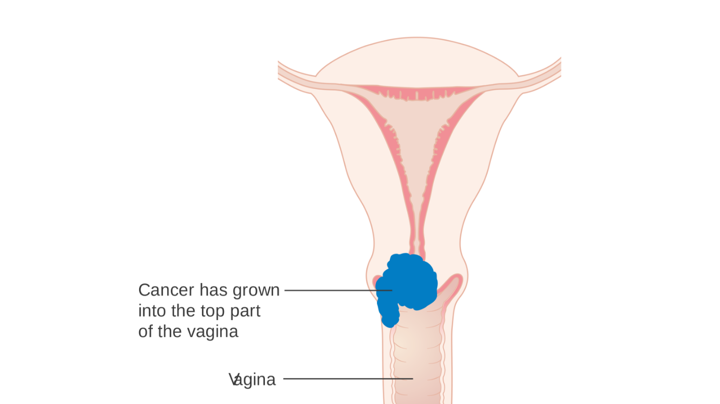
The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the organ where a fetus grows). The cervix leads from the uterus to the vagina (birth canal).
Cervical cancer starts in the cells lining the cervix -- the lower part of the uterus (womb). The fetus grows in the body of the uterus (the upper part).
Long-lasting infections with certain types of the STI human papillomavirus (HPV) [l1] cause almost all cases of cervical cancer.
Can cervical cancer be found early?
The best way to find cervical cancer early is to have regular screening with a Pap test (which may be combined with a test for human papilloma virus or HPV). Early detection greatly improves the chances of successful treatment and prevents any early cervical cell changes from becoming cancerous. Having a Pap test is to check for abnormal cells in the cervix or a test to check for HPV can find cells that may become cervical cancer. These cells can be treated before cancer forms.
Vaccines that protect against infection with these types of HPV can greatly reduce the risk of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer can usually be cured if it is found and treated in the early stages.
In Myanmar, not many facilities offer HPV testing as of 2015. It is only available at some private hospitals and large general hospitals in the big cities.
