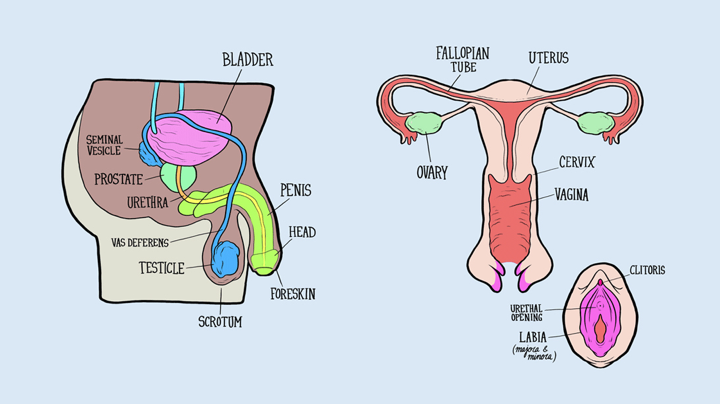
External Anatomy
- VULVA
- All of the external organs of the female reproductive system
The Labia or Lips: They are the outer part of your genitals which act as covering or protection for your private part. The way they look is different from one lady to another. It is almost always covered in hair-pubic hair. Some women’s labia may be a little longer than others but that poses no problem. But if your labia is long enough to cause you major discomfort when you put on your underwear, then you should speak to your doctor or healthcare provider about it.
- Protects internal organs against infectious diseases
- Functions in sexual arousal
- There are two parts named : Labia Majora and Labia Minora
Hymen
- Located just inside the vaginal opening
- Thin tissue stretching across the opening
- usually has several holes with defferent shapes
- Allows passage of menstrual blood
- 1ST time intercourse – female may experience pain & bleeding, NOT ALWAYS true with all females!
- Tissue is very flexible & may stay intact during intercourse!
- You can get pregnant & still have hymen intact!
Clitoris
- Small knob of tissue above & in front of vaginal opening
- Rich supply of nerve endings & blood vessels
- Important in sexual arousal
- Similar in sensitivity & # of nerve endings to head of penis
INTERNAL ANATOMY
Vagina
- Elastic tube-like pathwayUp to 6” long At rest, walls of vagina touch
- During arousal, they expand to allow penis to enter
- If not ready/aroused, walls of vagina will tear
- Capable of stretching to allow birth
Cervix
The tube at the end of the vagina that connects the vagina to the uterus. The cervix is shaped like a donut.
Uterus This organ is where fetus (or) babies grow until they are ready to be born. Its position is between the cervix and the fallopian tubes. It’s in the lower part of the pelvis.
- Strong elastic muscle; about the size of a fist
- hold & nourish developing embryo & fetus
- Endometrium
- Inner lining of uterus
- Rich supply of blood vessels
Builds up with blood tissue to prepare for a possible pregnancy
Fallopian Tubes
- They are the roads that the eggs (ova) travel through from the ovaries to the womb(uterus)
- Tubes on each side of the uterus and Leads to ovaries
- Fertilization usually occurs in the widest part of the fallopian tube
- Finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes called Fimbriae
- It surrounds the top part of each ovary and gathers the egg into the tube
OVARIES
- The store house for eggs that are not mature. When the eggs mature, they are released once every month.
2 main functions
- Housing the eggs for the ovulation
- Produce female sex hormones Estrogen & Progesterone
Ovulation
- Process of releasing one mature egg each month into that ovary’s fallopian tube
- A large number of immature eggs in ovaries at birth
- Hormones from pituitary cause ovaries to begin producing female sex hormones
- Eggs begin to mature
- An egg can live about 2 days in fallopian tube
